Cell Division and Cell Cycle:
 |
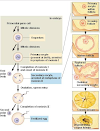
| Cell cycle and cell division |
Here in this article, we are going to explain two topics Cell division and cell cycle. Cell division is actually one of the stages of Cell Cycle. Therefore we are going to discuss cell division later after we explain cell cycle first.
Definition of Cell Cycle:
The time from the beginning of one cell division to the beginning of another cell division is called cell cycle.
The cell cycle is a series of events in a eukaryotic cell which results in its replication. A single cell fertilized egg develops into a mature organism by Cell Cycle.
The cell cycle comprises of two periods.
1. Interphase:
The most important event of interphase is the duplication of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid).
2. Cell Division:
During this phase, the cell split into two daughter cell.
We have explained this phase in detail after the end of cell cycle topic.
Interphase:
Interphase is the longest part of Cell Cycle. It is the period between the end of mitosis and the beginning of next prophase. Many important events occur during interphase.
Replication of DNA is the most important event of interphase.
Phases of Interphase:
Interphase consists of three sub-phases.
- G1-Phase
- S-Phase
- G2-Phase
a. G1-Phase:
G stand for Gap. It is the first and longest phase of the interphase. During this phase the newly produced cells grow in size and necessary preparation is done for DNA replication. RNA, Ribosomes and several Enzymes are synthesized during this phase.
The duration of G1-Phase may be from few hours to several days.
b. S-Phase:
It is regarded as the most vital event of Cell Cycle. Replication of DNA occurs during this phase. After DNA replication the cell contains twice the number of chromosomes. The duration of this phase is variable but is shorter than the G1 phase. When replication is completed it marks the end of the S-phase.
c. G2-Phase:
The period between the completion of DNA synthesis and beginning of active mitosis is the G2-Phase. During this phase, preparations take place for chromosomes condensation and construction of spindle fibers.
The final event occurs with the replication of centrioles.
You may also read:
- What is Cell and cell theory
- What Is Oogenesis | Prenatal And Postnatal Stages Of Oogenesis
- Gametogenesis | Spermatogenesis, And Spermiogenesis
2. Cell Division:
The division of a cell into daughter cells is called cell division.
The fertilized egg cell is the beginning of an organism. This fertilized egg cell multiply through cell division and add new cells. This process is continued and results in an adult human. An adult human has approximately 100,000 billion cell.
When a cell divides it grows in size and duplicates its chromosomes which on separation exactly distribute between the two daughter cells. The nucleus of each cell contains DNA located in 46 chromosomes.
There are two main types of cell division that is Mitosis and Miosis.





0 Comments